The Unveiling of the Debanking Effect – Examining the Winners and Losers in the Emerging Financial Landscape

The concept of debanking has become increasingly prevalent in today’s financial landscape, shaking the foundation of traditional banking systems. As technological advancements drive the rise of alternative financial solutions, questions arise regarding the winners and losers in this new paradigm.
Debanking, essentially, refers to the process of disintermediation, where individuals and businesses bypass traditional banking institutions to access financial services. This shift has been fueled by the emergence of fintech companies, peer-to-peer lending platforms, and cryptocurrencies, which offer faster, cheaper, and more accessible alternatives to traditional banking.
While debanking promises greater financial inclusion and convenience for some, it also raises concerns about the potential pitfalls and unintended consequences of this new financial landscape. Those who stand to benefit from debanking include the unbanked and underbanked populations, who now have easier access to basic financial services. Additionally, small businesses and startups can leverage alternative lending platforms to secure capital that may have been out of reach through traditional channels.
On the other hand, the rise of debanking could potentially leave certain groups behind. Traditional banks may face decreased relevance and profitability, leading to job losses and reduced economic stability. Additionally, the regulatory landscape surrounding debanking is still evolving, raising concerns about consumer protection and financial security.
In this article, we will delve deeper into the impact of debanking on different stakeholders and assess the overall implications of this new financial paradigm. By examining the winners and losers, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in the ever-evolving world of finance.
The Rise of Debanking
Debanking is the growing trend of individuals and businesses being excluded from traditional banking systems. With the rise of fintech and alternative financial services, many people are now turning to non-bank options for their financial needs. This shift is fueled by a variety of factors, including financial instability, high fees, and a lack of trust in traditional banks.
One of the key drivers of debanking is the desire for greater financial autonomy. People are looking for alternatives that allow them to have more control over their money, without having to rely on traditional banks. Fintech platforms that offer peer-to-peer lending, cryptocurrency exchanges, and digital wallets are gaining popularity as they provide individuals with more freedom and flexibility in managing their finances.
However, while debanking can provide many benefits, it also comes with risks. Without the oversight and regulatory protections provided by traditional banks, individuals and businesses may be more vulnerable to fraud, scams, and other financial crimes. It is crucial for consumers to be cautious and informed when using non-bank financial services.
The rise of debanking also has wider implications for the financial system as a whole. Traditional banks are facing increased competition from fintech companies, and this is forcing them to adapt and innovate in order to stay relevant. As a result, we are witnessing a shift towards digital banking and a greater emphasis on customer experience and convenience.
Furthermore, the rise of debanking is leading to a more inclusive financial ecosystem. It is allowing individuals who were previously excluded from the traditional banking system to access financial services and participate in the economy. This is particularly beneficial for underbanked and unbanked populations, who often face barriers to entry due to factors such as a lack of identification or credit history.
In conclusion, the rise of debanking is reshaping the financial industry and transforming the way we access and manage our finances. While it offers many advantages, it also requires consumers to be proactive in protecting themselves and their money. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, it is important for individuals and businesses to stay informed about the latest developments and make informed decisions about their financial choices. To learn more about debanking, visit exchange debank.
Understanding the Concept

The concept of debanking refers to the practice of excluding individuals or businesses from accessing traditional banking services. This exclusion can occur due to various reasons, including but not limited to a person’s financial history, creditworthiness, or the perceived risk associated with their activities.
Debanking can have significant consequences for individuals and businesses, as access to banking services is integral to participating in the modern economy. Without access to bank accounts, individuals may struggle to receive income, make payments, or save money. Similarly, businesses may face challenges in receiving and making payments, managing cash flow, or accessing credit.
The concept of debanking has gained attention in recent years due to the rise of alternative financial technologies and the increasing use of digital payment systems. While these innovations have brought convenience and expanded access to financial services for many, they have also contributed to the exclusion of certain individuals or businesses from the formal financial system.
It is important to understand the impact of debanking and its implications for various stakeholders. For individuals who are debanked, the consequences can be severe, leading to increased financial insecurity and limited opportunities for economic growth. At the same time, the practice of debanking can have unintended consequences for banks and financial institutions, as it may result in reputational risks, loss of potential customers, and the erosion of trust in the banking system.
By studying the concept of debanking and its effects, policymakers, researchers, and financial institutions can work towards developing inclusive financial systems that ensure equal access to banking services and address the underlying causes of debanking.
Reasons for Debanking
Debanking, the act of excluding individuals or businesses from the traditional banking system, can occur for a variety of reasons. The following are some of the main factors that contribute to debanking:
- Lack of documentation: Many individuals, particularly those in low-income or marginalized communities, may lack the necessary identification or documentation required by banks to open accounts. Without access to basic banking services, these individuals are forced to rely on alternative financial providers.
- Poor credit history: Individuals with a history of financial mismanagement, defaults, or bankruptcies may be debanked due to their high risk profile. Banks often view these individuals as a potential liability and prefer to exclude them from their customer base.
- Business risk: Small businesses that operate in industries considered high-risk, such as gambling or adult entertainment, may be debanked by traditional financial institutions. These businesses are often seen as a reputational risk for banks and are therefore denied access to banking services.
- Geographic limitations: In some regions, particularly rural areas, there may be a lack of banking infrastructure or a limited number of branch locations. This can result in individuals and businesses being unable to access banking services, ultimately leading to debanking.
- Compliance and regulatory issues: Banks are subject to strict regulatory requirements and must comply with anti-money laundering (AML) and know your customer (KYC) regulations. When customers are unable to meet these requirements or banks identify potential compliance risks, they may choose to debank these individuals or businesses.
Debanking can have significant consequences for individuals and businesses, as it limits their ability to access essential financial services and participate fully in the economy. Understanding the reasons for debanking is crucial in addressing these issues and working towards a more inclusive financial system.
Implications for the Economy
The debanking phenomenon, with its far-reaching impact on individuals and businesses, has several implications for the economy as a whole. These implications can have both positive and negative consequences, depending on the perspective.
1. Financial Inclusion vs. Exclusion
One of the main implications of debanking is the potential for increased financial exclusion. As traditional banking services become less accessible for certain individuals and businesses, they may be pushed into alternative financial channels that are less regulated and more susceptible to fraud and exploitation. This could hinder economic development and perpetuate cycles of poverty.
However, on the flip side, the rise of decentralized finance and alternative financial services can also promote financial inclusion. By leveraging technology, individuals and businesses that were previously excluded from the traditional banking system can now access financial services, such as loans, insurance, and investments, through peer-to-peer platforms and cryptocurrencies. This can stimulate economic growth and empower marginalized communities.
2. Disruption of Traditional Banking

The debanking trend poses a significant disruption to traditional banking models. As more individuals and businesses turn to decentralized financial systems, traditional banks may face challenges in attracting and retaining customers. This could lead to a decrease in profitability and potentially result in layoffs and branch closures.
However, this disruption also presents opportunities for traditional banks to adapt and evolve. By embracing technological advancements and collaborating with emerging fintech companies, banks can stay relevant in the new financial paradigm. This can drive innovation, enhance customer experience, and foster healthy competition within the industry.
3. Systemic Risks and Regulatory Challenges
The shift towards decentralized finance introduces new systemic risks and regulatory challenges for the economy. With less oversight and regulation, there is a higher potential for fraud, money laundering, and other illicit activities. This can undermine trust in the financial system and pose risks to financial stability.
Regulators will need to adapt their frameworks and develop new strategies to address these challenges effectively. This includes finding the right balance between promoting innovation and protecting consumers, as well as enhancing cross-border collaboration to manage the global nature of decentralized finance.
In conclusion, the debanking trend has profound implications for the economy. It can promote financial inclusion and innovation while disrupting traditional banking models. However, it also introduces risks that need to be carefully managed through regulatory measures. As the new financial paradigm continues to evolve, it is crucial for stakeholders to collaborate and find solutions that maximize the benefits while mitigating the risks.
The Winners of Debanking
In the new financial paradigm of debanking, there are winners and losers. While some individuals may be negatively impacted by this shift, certain entities stand to benefit greatly. Here are the winners of debanking:
Fintech Companies
Fintech companies are at the forefront of the debanking movement. They have been able to leverage technological advancements to provide innovative financial solutions that bypass traditional banks. By offering low-cost services, streamlined processes, and personalized experiences, fintech companies are able to attract customers who have been turned away or overlooked by traditional banks.
Micro and Small Businesses
Micro and small businesses are often underserved by traditional banks due to various reasons such as lack of collateral, limited credit history, or being in the informal sector. However, in the new financial paradigm, these businesses stand to benefit. Fintech companies offer more accessible lending options, such as peer-to-peer lending or crowdfunding, which can provide much-needed capital for these businesses to grow and thrive.
Unbanked Individuals
Debanking has the potential to empower unbanked individuals by giving them access to financial services that were previously out of reach. Fintech companies are finding innovative ways to bridge the gap and offer basic banking services to those who have been excluded from the traditional banking system. Mobile banking apps, digital wallets, and microfinance platforms are some of the tools that are making financial inclusion a reality for unbanked individuals.
Emerging Markets
Emerging markets often face challenges in establishing a robust banking infrastructure. However, the debanking trend is opening up new opportunities for these markets to leapfrog traditional banking systems and adopt more efficient and inclusive financial technologies. Fintech companies are able to tap into these markets and provide much-needed access to financial services, promoting economic growth and development.
In conclusion, while debanking brings about significant changes in the financial landscape, it also creates winners. Fintech companies, micro and small businesses, unbanked individuals, and emerging markets all stand to gain from the new financial paradigm.
Empowering the Unbanked
Access to financial services has traditionally been limited to those who have a bank account. However, the rise of technology and the advent of decentralized finance (DeFi) are now creating opportunities for the unbanked population to participate in the global financial system.
By leveraging blockchain technology, cryptocurrencies, and smart contracts, DeFi platforms are enabling individuals without traditional bank accounts to access financial services such as loans, savings accounts, and investment opportunities. This not only provides them with the means to securely store and transact value but also empowers them to build wealth and improve their economic stability.
Moreover, DeFi platforms are often more inclusive and accessible compared to traditional banking systems. They do not require extensive documentation or credit history checks, making it easier for the unbanked to get started. Additionally, these platforms operate 24/7 and are not constrained by geographical boundaries, allowing individuals from anywhere in the world to participate.
Furthermore, DeFi puts the power back into the hands of the unbanked by removing the need for intermediaries, such as banks or financial institutions. Transactions occur directly between peers, ensuring greater transparency and reducing the risk of fraud or manipulation. The use of smart contracts also eliminates the need for trust, as the terms of the agreements are enforced automatically.
Overall, empowering the unbanked through DeFi has the potential to transform the lives of millions of people around the world. By providing access to financial services and opportunities for wealth creation, societies can become more inclusive and individuals can achieve greater economic independence.
Growth of Alternative Financial Services
As traditional banking becomes increasingly inaccessible for certain individuals and communities, the demand for alternative financial services has been on the rise. These services, often referred to as “unbanked” or “underbanked” services, provide financial products and solutions to individuals who have limited or no access to traditional banking services.
One key driver of the growth of alternative financial services is technological advancements. The widespread adoption of smartphones and the internet has enabled financial service providers to reach a larger customer base, including those in underserved areas. Mobile banking apps, online marketplaces, and peer-to-peer lending platforms are just a few examples of alternative financial services that have gained popularity.
Another factor contributing to the growth of alternative financial services is the desire for greater convenience and flexibility. Traditional banking services often require customers to adhere to strict operating hours and visit physical branches, which can be inconvenient for many individuals. In contrast, alternative financial services offer round-the-clock access to financial products and services through digital platforms, allowing customers to manage their finances at their own pace.
The growth of alternative financial services also stems from the changing needs and preferences of consumers. Many individuals, particularly millennials, prioritize convenience, transparency, and personalized experiences when it comes to financial services. Alternative financial service providers cater to these preferences by offering user-friendly interfaces, simplified account management, and customized product offerings.
Moreover, alternative financial services have also emerged as a viable solution for individuals who have been excluded from the traditional banking system due to factors such as poor credit history, lack of documentation, or low income. These services often have relaxed eligibility criteria and offer products such as prepaid debit cards, check cashing services, and microloans, which provide access to basic financial services without requiring a traditional bank account.
Overall, the growth of alternative financial services is driven by the need to address the financial exclusion experienced by certain individuals and communities. By offering accessible, convenient, and tailored financial solutions, these services play a crucial role in promoting financial empowerment and inclusion.
Disrupting Traditional Banking Models
In the era of digital innovation, traditional banking models are being disrupted by emerging technologies and new players in the industry. Fintech startups and alternative financial service providers are challenging the status quo and reshaping the way we think about banking.
One of the key advantages of these disruptive models is their ability to provide innovative solutions to longstanding problems in the traditional banking system. For example, traditional banks often require extensive documentation and collateral for loan applications, making it difficult for individuals and small businesses to access credit. Fintech platforms, on the other hand, use alternative data sources and sophisticated algorithms to assess creditworthiness, making the process faster and more inclusive.
Furthermore, traditional banks have traditionally been slow to adopt new technologies and adapt to changing customer needs. This has created a gap in the market that fintech companies have been quick to fill. With their user-friendly interfaces, mobile banking apps, and personalized financial advice, these disruptive players are making banking more accessible and convenient for consumers.
However, disrupting traditional banking models also comes with its own set of challenges and risks. As the industry becomes more crowded and competitive, it becomes harder for individual fintech firms to differentiate themselves and gain market share. Additionally, regulatory oversight and compliance requirements pose a significant burden for these disruptive players, potentially limiting their growth and innovation.
While the future of traditional banking models remains uncertain, it is clear that the industry is undergoing a transformation. Whether it is through increased collaboration between traditional banks and fintech startups or the rise of entirely new banking ecosystems, change is on the horizon, and it is imperative for all stakeholders to adapt and evolve.
The Losers of Debanking
In the new financial paradigm of debanking, there are clear winners and losers. While some individuals and institutions stand to benefit from this shift, there are others who are negatively impacted and find themselves at a distinct disadvantage. Here, we delve into the various groups that are likely to be the losers in this new era.
1. Unbanked individuals
The unbanked individuals, who do not have access to traditional banking services, are some of the biggest losers in the debanking trend. Without access to banking services, such as savings accounts, loans, and credit cards, these individuals are unable to participate fully in the financial system. This lack of access can limit their opportunities for financial growth and stability, making it difficult for them to save, invest, and build credit.
2. Small businesses
Small businesses also suffer as a result of debanking. Many small businesses rely on traditional banking services to manage their finances, process payments, and secure loans for growth and expansion. Without access to these services, they may struggle to maintain their operations and compete with larger companies. The debanking trend can also limit their ability to access credit, hindering their growth and potentially leading to closures.
| Unbanked Individuals | Small Businesses | Rural Communities |
|---|---|---|
| • Lack of access to financial services | • Difficulty managing finances and securing loans | • Limited access to banking infrastructure |
| • Reduced opportunities for financial growth | • Struggles to compete with larger companies | • Hindered economic development |
| • Difficulty saving, investing, and building credit | • Hindered growth and potential closures | • Limited access to capital and financial services |
3. Rural communities
Rural communities often face limited access to banking infrastructure and financial services even in the traditional banking system. With the debanking trend, this situation can further worsen for these communities. The closure of physical bank branches and the shift towards online and digital banking can leave rural communities with even fewer options for accessing essential financial services. This limited access can hinder economic development, limit opportunities for growth, and exacerbate existing inequalities.
In conclusion, while there are winners in the debanking trend, it is essential to recognize the groups that are at a disadvantage. Unbanked individuals, small businesses, and rural communities are some of the losers in this new financial paradigm. Efforts should be made to address their needs and ensure that they have access to the financial services necessary for economic growth and stability.
Impact on Traditional Banks
As the new financial paradigm takes hold, traditional banks are faced with numerous challenges and opportunities. On one hand, they risk losing customers to debanking alternatives that offer greater convenience, lower fees, and more tailored financial services. This threat is particularly significant for banks that have been slow to adapt to digital transformation.
However, traditional banks can also benefit from the shift towards debanking. By embracing technology and innovation, they can enhance their competitive position and attract new customers. Some banks may choose to partner with fintech companies or launch their own digital platforms to meet the changing needs and preferences of consumers.
Challenges for Traditional Banks
The rise of debanking poses several challenges for traditional banks. First, they must contend with a loss of market share as more customers opt for alternative financial services. This could lead to a decrease in deposits and lending activity, affecting their profitability and ability to generate revenue.
Second, traditional banks face increased pressure to improve their digital offerings and customer experience. Many customers now expect the same level of convenience and functionality that digital banks and fintech companies provide. Banks must invest in technology infrastructure and talent to remain competitive in this evolving landscape.
Opportunities for Traditional Banks
While debanking presents challenges, it also offers opportunities for traditional banks to evolve and thrive. By leveraging their existing customer base and credibility, banks can introduce innovative solutions that combine the best aspects of digital and traditional banking.
Additionally, traditional banks have the advantage of established regulatory frameworks and risk management systems. This can give them a competitive edge over emerging fintech players that may still be navigating regulatory hurdles.
In conclusion, the impact of debanking on traditional banks is complex and multifaceted. While it poses challenges, it also opens doors for innovation and growth. The banks that successfully adapt and embrace the new financial paradigm will be the winners in this evolving landscape.
The Wealth Divide
One of the significant impacts of debanking is the widening wealth divide. As traditional banking services become less accessible, individuals with lower incomes and limited financial resources are disproportionately affected. These individuals often rely on traditional banking services for basic financial transactions, such as cashing checks, paying bills, and accessing credit.
The Unbanked and Underbanked:
The unbanked, referring to those without a bank account, and the underbanked, referring to those who have limited access to banking services, are particularly vulnerable to the debanking trend. Without access to affordable banking options, these individuals may turn to alternative financial services, such as payday lenders, pawnshops, and check-cashing services, which often come with exorbitant fees and high-interest rates.
As a result, the wealth gap between the unbanked and underbanked and those who have access to traditional banking services continues to grow. Without access to banking services, individuals in these underserved communities struggle to save money, build credit, and invest in their future.
The Digital Divide:
The rise of digital banking further exacerbates the wealth divide. As more financial institutions move to online platforms, individuals without internet access or digital literacy skills face barriers to entering the digital financial ecosystem. This digital divide disproportionately affects low-income communities, rural areas, and older generations.
Those who are unable to access digital banking services miss out on the convenience, cost savings, and financial innovation that come with these platforms. They may also face difficulties in accessing government benefits and stimulus payments that are increasingly being distributed electronically.
The Need for Inclusive Solutions:
To address the widening wealth divide caused by debanking, inclusive solutions are needed. It is crucial to ensure that everyone, regardless of income level or location, has access to affordable and reliable banking services.
This can be achieved through initiatives such as community banking programs, mobile banking solutions, and financial literacy programs targeting underserved communities. By promoting financial inclusion and providing equal opportunities for wealth creation, we can counteract the negative effects of debanking and work towards a more equitable financial system.
Regulatory Challenges
As debanking continues to gain momentum in the new financial paradigm, regulatory bodies are faced with a number of challenges. The decentralized nature of many digital currencies and blockchain-based financial systems presents a unique set of hurdles for traditional regulatory frameworks.
First and foremost, the global nature of debanking means that regulations must be coordinated across jurisdictions. This requires international cooperation and a standardized approach to addressing the risks and benefits of debanking. Without international alignment, regulatory arbitrage and loopholes may emerge, potentially leading to a fragmented and ineffective regulatory landscape.
Furthermore, the anonymity and pseudonymity offered by some digital currencies make it difficult for regulators to trace and monitor financial transactions. This presents challenges in terms of preventing money laundering, terrorist financing, and other illicit activities. Regulators must find innovative ways to strike a balance between privacy and security, ensuring that criminals are apprehended while protecting the privacy and rights of legitimate users.
In addition, the rapid pace of technological advancement in the debanking space means that regulators must constantly update their knowledge and understanding. This requires ongoing education and collaboration with industry players to keep up with the evolving landscape. Failure to do so may result in outdated regulations that do not adequately address emerging risks.
Lastly, regulatory challenges extend beyond digital currencies to include other aspects of the new financial paradigm, such as decentralized lending platforms and decentralized exchanges. These platforms operate outside of traditional financial intermediaries, presenting regulatory gaps and uncertainties. Regulators must work to close these gaps and ensure the stability and integrity of the financial system.
Overall, regulatory challenges in the new financial paradigm are complex and multifaceted. Addressing these challenges requires a proactive and collaborative approach among regulators, industry players, and international bodies. Only through effective regulation can the potential benefits of debanking be fully realized while mitigating risks and protecting the interests of all stakeholders.
Future Outlook
The debanking trend is expected to continue shaping the financial landscape in the coming years. As more and more individuals and businesses are being denied access to traditional banking services, alternative financial solutions will gain popularity and prominence.
One possible outcome of debanking is the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms. These platforms leverage blockchain technology to provide financial services without the need for intermediaries. As individuals explore alternative options outside of traditional banking, DeFi can offer a decentralized and transparent way to access loans, save money, and invest.
Another potential development is the growth of digital banking solutions. With the increasing use of smartphones and internet connectivity, digital banking has seen significant growth in recent years. Debanking may accelerate this trend, as individuals seek out convenient and accessible financial solutions that do not rely on traditional banks.
Risks and Challenges
While debanking can open up new opportunities, it also poses risks and challenges. Without the regulations and protections offered by traditional banking institutions, individuals may be more vulnerable to fraud and scams. Additionally, the lack of oversight and accountability in alternative financial solutions can lead to market instability and financial instability.
Furthermore, there may be a widening financial inclusion gap as certain groups and communities are disproportionately affected by debanking. Vulnerable populations, such as low-income individuals and those without access to reliable internet or technology, may struggle to find alternative financial services that meet their needs.
Policy Implications
With the increasing prevalence of debanking, policymakers will need to adapt regulations to ensure consumer protection and financial stability. They will also need to foster innovation and competition in the financial sector to encourage the development of alternative financial solutions that are accessible, affordable, and safe for all individuals.
Efforts should be made to bridge the digital divide and ensure that those without access to technology or reliable internet can still access financial services. This may involve investing in infrastructure and providing education and support to underserved communities.
- Collaboration between traditional banks and alternative financial service providers can also be fruitful, as it can combine the strengths of both approaches and provide a more inclusive and diverse range of financial products and services.
- Overall, the future outlook for debanking is a mixture of opportunities and challenges. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, it is important to prioritize the needs of individuals and communities, ensuring that everyone has equitable access to the financial services they require.
The Shifting Financial Landscape
In today’s interconnected world, the financial landscape is constantly evolving. Traditional banking institutions are no longer the only option for individuals and businesses seeking financial services. The rise of technology and the internet has brought about a new era of financial innovation and disruption. As a result, the traditional banking model is being challenged and transformed.
One major trend in this shifting financial landscape is the concept of “debanking.” Debunking refers to the process of individuals and businesses being excluded from the traditional banking system for various reasons, such as a poor credit history or the inability to meet strict banking requirements. This exclusion has led to the emergence of alternative financial technologies and services, which aim to provide banking services to those who have been debanked.
The Rise of Fintech
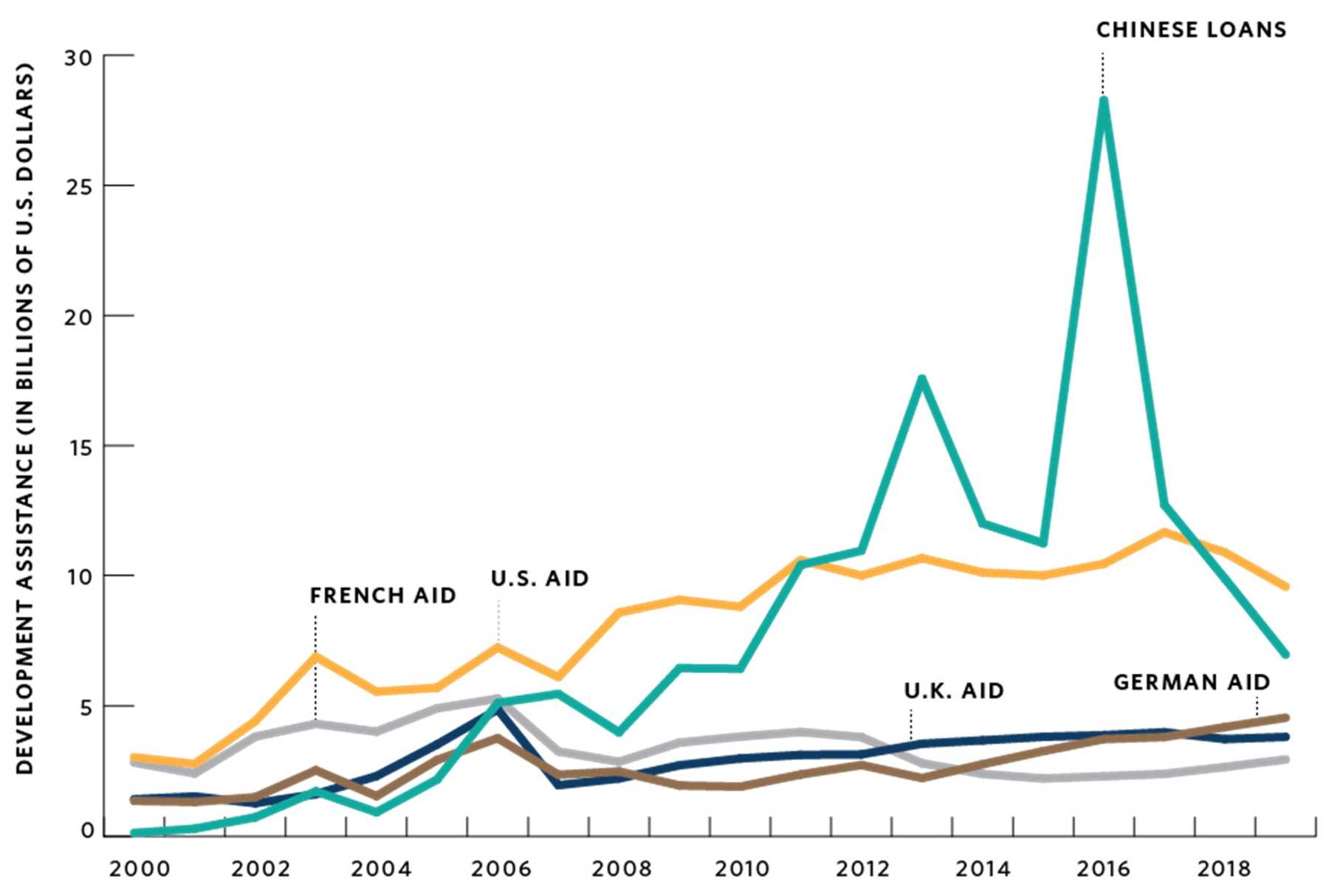
One of the key players in this new financial paradigm is the rise of financial technology, or fintech, startups. Fintech companies use cutting-edge technology to provide financial services that are often more accessible, efficient, and flexible than traditional banking institutions. These companies often leverage mobile apps, artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and other innovations to offer services such as digital payments, lending, investment management, and more.
Fintech startups have greatly benefited from the debanking trend, as they are able to fill the gap left by traditional banks and provide financial services to individuals and businesses previously excluded from the system. This has led to increased competition in the financial industry and has forced traditional banks to adapt and innovate to stay relevant.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the shifting financial landscape brings many opportunities for innovation, it also poses challenges for individuals and businesses. The new financial paradigm may not be suitable or accessible for everyone, especially those who struggle with technology or lack access to the internet. Additionally, the rapid pace of technological advancement raises concerns about data privacy and security.
However, for those who are able to navigate this new financial landscape, there are many benefits to be gained. Access to alternative financial services can provide individuals and businesses with greater financial inclusion, lower costs, faster transactions, and more personalized services. The shifting financial landscape has the potential to level the playing field and empower those who have been historically underserved by the traditional banking system.
- Increased competition in the financial industry
- Greater financial inclusion
- Lower costs and faster transactions
- Personalized services
- Empowerment of underserved individuals and businesses
In conclusion, the shifting financial landscape is transforming the traditional banking model and opening up new opportunities and challenges. Fintech startups and alternative financial services are providing innovative solutions to individuals and businesses previously excluded from the banking system. While there are concerns about accessibility and security, the potential benefits of this new paradigm are significant. As technology continues to advance, the financial landscape will continue to shift, and it is up to individuals and businesses to adapt and take advantage of the opportunities presented.
FAQ:,
What is debanking?
Debanking refers to the process of excluding individuals or businesses from accessing traditional banking services, such as loans, accounts, and credit cards. It usually happens when financial institutions terminate or deny services to certain customers due to various reasons, such as high-risk profiles, regulatory compliance issues, or a history of non-payment.
What are the consequences of debanking?
The consequences of debanking can be severe for those who are excluded from the traditional banking system. They may face difficulties in accessing credit, managing their finances, and participating in the economy. It can also have a negative impact on their credit scores and overall financial well-being. Additionally, debanking can lead to a growing reliance on alternative financial services, such as payday lenders, which often charge high interest rates and fees.