Who benefits from the democratization of finance? Examining debanking and financial inclusion

In recent years, there has been a growing trend towards debanking and the democratization of finance. This movement seeks to challenge the traditional banking system, which has long been criticized for its exclusionary practices and lack of accessibility. With the rise of new technologies and innovative financial services, the power is shifting towards individuals and communities, empowering them to take control of their own financial lives.
Debanking refers to the process of removing the traditional intermediaries, such as banks, from the financial system. Instead, individuals can now access financial services directly through digital platforms and virtual currencies. This shift has opened up a whole new world of opportunities for those who were previously excluded from the traditional banking system.
The democratization of finance aims to break down the barriers that have traditionally prevented marginalized communities from accessing financial services. This includes individuals who are unbanked or underbanked, as well as those who face discrimination or limited opportunities due to their socio-economic status. By giving them the tools and resources they need to participate in the global economy, debanking and financial inclusion can help bridge the gap between the rich and the poor, empowering individuals to build a better future for themselves and their communities.
However, as with any major societal shift, there are both benefits and challenges associated with debanking and the democratization of finance. While it can provide greater access to financial services and promote economic empowerment, there are concerns about privacy, security, and regulatory oversight. It is important to strike a balance between innovation and consumer protection, ensuring that individuals have the necessary safeguards in place to protect their financial interests without stifling the potential for growth and innovation.
In conclusion, debanking and financial inclusion have the potential to revolutionize the way we think about and interact with our financial system. By removing barriers and empowering individuals, this movement can bring about greater economic equality and opportunity for all. However, it is crucial that we approach this transition with caution and foresight, taking into account the potential risks and challenges that may arise along the way.
The concept of debanking
Debanking refers to the process of excluding individuals or businesses from accessing banking services. This exclusion can be due to various factors such as low creditworthiness, lack of proper identification documents, or not meeting the minimum income requirements set by traditional financial institutions.
The concept of debanking has gained attention as fintech companies and alternative financial institutions have emerged to provide financial services to those who have been excluded from the traditional banking system. These fintech platforms often use technology and innovative approaches to make financial services more accessible and affordable.
Debanking is seen as a double-edged sword. On the one hand, it can exclude marginalized communities and individuals from participating fully in the economy. This can exacerbate income inequality and hinder financial inclusion. On the other hand, debanking can also be seen as an opportunity for innovation and democratization of finance.
One example of finance debank is debank.lu, a platform that aims to provide transparent and affordable financial services to individuals and businesses. The platform utilizes blockchain technology to enable faster transactions and lower costs compared to traditional banking systems.
By leveraging technology and reimagining banking processes, debanking can provide opportunities for individuals and businesses who have been left out of the traditional banking system. It can empower them to access financial services, build credit, and participate more actively in the economy.
The impact of debanking on financial inclusion
Debanking refers to the practice of excluding individuals or communities from access to traditional banking services. This exclusion can have far-reaching implications for financial inclusion, which seeks to ensure that all individuals and communities have access to the formal financial system.
One of the key impacts of debanking on financial inclusion is the hindrance it poses to economic growth and development. Without access to basic financial services such as savings accounts, credit, and insurance, individuals and communities are unable to participate fully in economic activities. This lack of access hampers their ability to save, invest, and borrow money, which in turn limits their potential for economic prosperity.
In addition to hindering economic growth, debanking also exacerbates existing inequalities. Those who are most likely to be affected by debanking include low-income individuals, migrants, refugees, and rural communities. These groups often already face significant barriers to financial inclusion, and debanking further limits their opportunities for social and economic advancement.
Furthermore, debanking can have negative implications for financial stability. Without access to formal banking services, individuals are more likely to turn to alternative financial services, such as predatory lenders and loan sharks. These informal financial channels often charge exorbitant interest rates, deepening individuals’ financial vulnerabilities and potentially leading to cycles of debt.
The impact of debanking on financial inclusion extends beyond individuals and communities. It also affects the broader economy by constraining the flow of capital and stifling innovation. Without access to formal banking services, entrepreneurs and small businesses may struggle to secure the capital needed to start or expand their ventures. This limitation on access to financing hampers innovation and hinders economic growth.
In conclusion, debanking has a profound impact on financial inclusion. It hampers economic growth, exacerbates inequalities, threatens financial stability, and stifles innovation. Addressing debanking is crucial for achieving inclusive economic development and ensuring that everyone has an equal opportunity to participate in and benefit from the financial system.
The role of fintech in debanking
Fintech, or financial technology, plays a significant role in the process of debanking and promoting financial inclusion. Fintech refers to the use of technology to provide innovative financial services and products. By leveraging technology, fintech companies are able to address the gaps in traditional banking systems and provide access to financial services to underserved populations.
1. Increased accessibility
Fintech has revolutionized the way financial services are accessed. Traditional banks often have physical branches that may not be easily accessible to individuals living in remote or rural areas. Fintech platforms, on the other hand, can be accessed through mobile phones or the internet, enabling individuals to conduct financial transactions from the comfort of their own homes. This increased accessibility removes barriers and allows individuals who were previously unbanked or underbanked to participate in the financial system.
2. Lower costs
Another significant advantage of fintech in debanking is the reduction in costs associated with financial services. Traditional banks often have high overhead costs due to the need for physical branches and a large workforce. Fintech companies, however, operate in a digital environment which significantly reduces their operational costs. These cost savings can be passed on to consumers, making financial services more affordable and accessible to individuals with limited financial resources.
In addition, fintech platforms often offer innovative solutions that bypass traditional intermediaries, such as remittance services that allow individuals to send and receive money directly without the need for costly remittance agents. This not only reduces costs but also increases the efficiency and speed of financial transactions.
3. Customized solutions
Fintech companies have the ability to leverage data and technology to develop customized financial solutions that cater to the specific needs of underserved populations. Traditional banks may not have the same level of flexibility and agility to adapt to the diverse needs of different customers. Fintech platforms can use data analysis to understand the financial behaviors and needs of individuals and offer personalized services that address their unique circumstances.
For example, fintech companies can provide microloans to small business owners who may not qualify for traditional loans due to limited credit history or collateral. This enables small businesses to access the capital they need to grow and expand, ultimately promoting economic development and financial inclusion.
In conclusion, fintech plays a crucial role in debanking by increasing accessibility, lowering costs, and providing customized solutions. It has the potential to bridge the gap between traditional banking systems and underserved populations, ultimately promoting financial inclusion for all.
The benefits of financial inclusion
Financial inclusion refers to the accessibility and availability of financial services to individuals and businesses, especially those in underserved and marginalized communities. This inclusion goes beyond merely having a bank account; it encompasses a wide range of financial services such as credit, insurance, and savings products.
1. Economic growth and poverty reduction
Financial inclusion plays a crucial role in promoting economic growth and reducing poverty. When individuals and businesses have access to financial services, they can save, invest, and utilize credit to improve their financial situation. This, in turn, leads to increased economic activity, job creation, and ultimately a decrease in poverty levels.
2. Empowerment of individuals and communities
Financial inclusion empowers individuals and communities by giving them the tools and resources they need to manage their finances effectively. With access to banking services, individuals can better plan for the future, set financial goals, and protect themselves and their assets against unexpected events. This empowerment allows individuals to have greater control over their financial lives and improves their overall well-being.
3. Reduction in inequality
Financial inclusion can help reduce income and wealth inequality within societies. By providing individuals with equal access to financial services, regardless of their socioeconomic background, financial inclusion works towards leveling the playing field and creating opportunities for everyone. This can lead to a more equitable society where all individuals have a fair chance at achieving economic success.
4. Enhanced financial stability
When more individuals and businesses have access to formal financial services, it contributes to overall financial stability. It reduces the risk of individuals resorting to informal or predatory lenders, which can result in high interest rates and debt traps. Furthermore, financial inclusion enables individuals to build a credit history and access affordable credit, reducing their vulnerability to financial shocks and emergencies.
Overall, the benefits of financial inclusion are far-reaching and extend beyond the individuals and communities directly involved. It has the potential to drive economic growth, empower individuals, reduce inequality, and enhance financial stability for the greater good of society as a whole.
Increased accessibility to financial services
One of the key benefits of debanking and the democratization of finance is increased accessibility to financial services. Traditionally, many individuals, particularly those in marginalized or underserved communities, have faced significant barriers to accessing basic financial services such as banking, credit, and insurance.
The rise of fintech and digital banking has drastically changed the landscape of financial services, making them more accessible to a wider range of people. With the increasing availability of smartphones and internet access, individuals can now access and manage their finances from the comfort of their own homes or on the go.
Furthermore, the elimination of physical branch locations and the reliance on digital platforms have also reduced the need for extensive documentation and paperwork, making it easier for individuals without formal identification or a credit history to access financial services.
In addition, debanking has opened up opportunities for new financial service providers to enter the market and offer products tailored to the specific needs of underserved populations. For example, microfinance institutions and peer-to-peer lending platforms have emerged to address the financing needs of small businesses and individuals who were previously excluded from traditional banking institutions.
| Benefits of increased accessibility to financial services: | |
|---|---|
| 1. Financial inclusion: | By increasing accessibility to financial services, debanking helps promote financial inclusion, allowing individuals from all walks of life to participate in the formal financial system and access opportunities for wealth creation and economic stability. |
| 2. Education and empowerment: | Accessible financial services can empower individuals by providing them with the knowledge, tools, and resources to make informed financial decisions, manage their money effectively, and plan for the future. |
| 3. Economic growth: | When more individuals have access to financial services, it can contribute to economic growth by stimulating increased savings, promoting entrepreneurship, and facilitating investment in productive activities. |
In conclusion, increased accessibility to financial services through debanking and the democratization of finance has the potential to transform the lives of individuals and communities, particularly those who have historically been excluded from the formal financial system. By breaking down barriers and providing equal opportunities for financial access and inclusion, debanking can contribute to a more equitable and prosperous society.
Empowerment of marginalized communities
One of the key benefits of debanking and the democratization of finance is the empowerment of marginalized communities. In traditional banking systems, people who are from lower-income backgrounds or have limited access to financial resources often face significant barriers in accessing basic banking services, credit, and loans. This lack of access further perpetuates social and economic inequalities.
By embracing alternative financial systems like decentralized finance (DeFi), marginalized communities can overcome these barriers and gain greater financial autonomy. DeFi platforms operate on blockchain technology and offer a range of financial services without requiring intermediaries like banks. This opens up new opportunities for individuals and communities to participate in the global financial system.
Access to basic banking services
The debanking movement aims to provide access to basic banking services to marginalized communities that are systematically excluded from the traditional banking system. DeFi platforms offer services like digital wallets, peer-to-peer lending, and remittance services, allowing individuals to send, receive, and store money without relying on traditional banks. This enables the unbanked and underbanked populations to participate in the economy and manage their finances more effectively.
Access to credit and loans
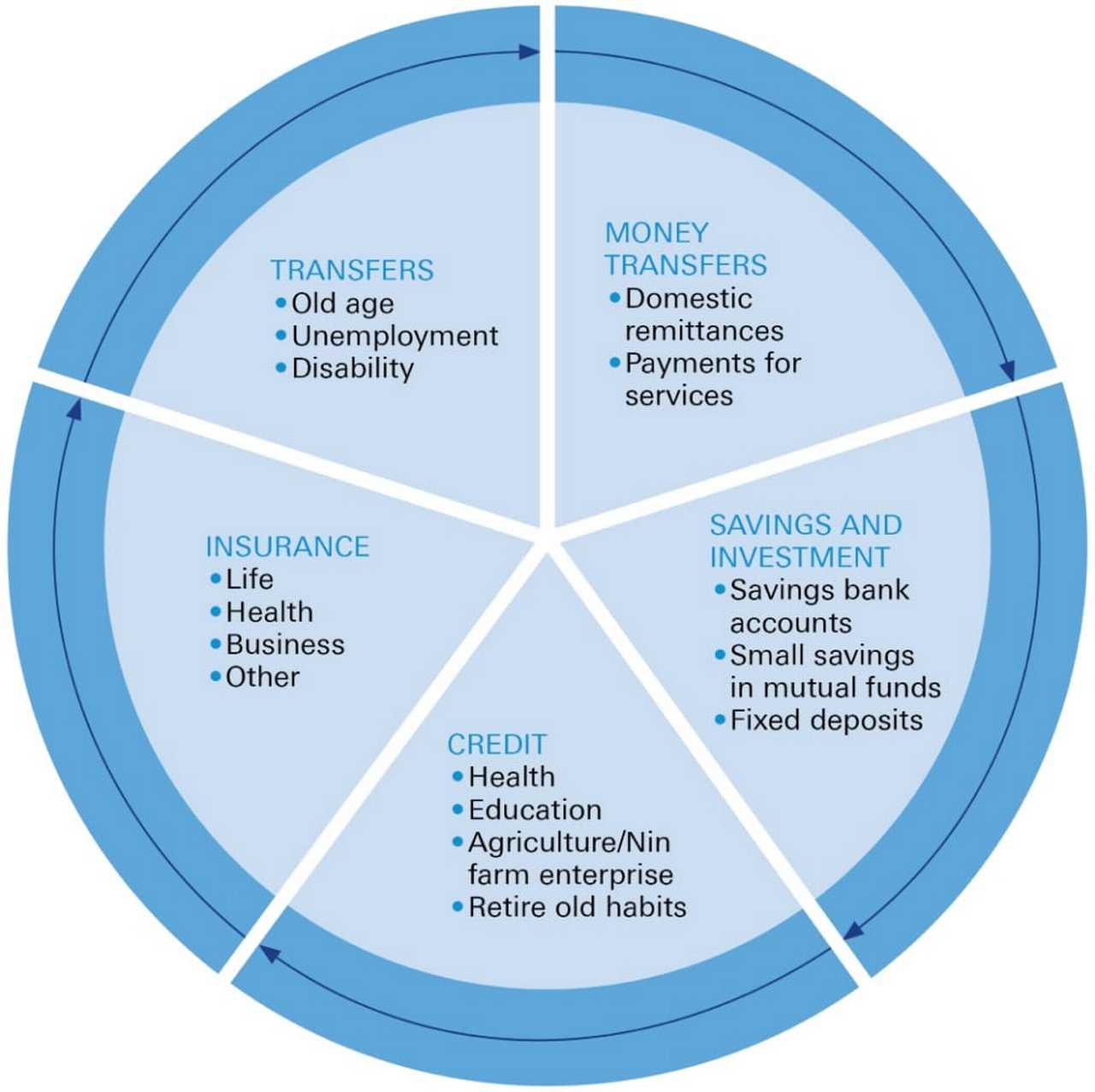
Access to credit and loans is crucial for individuals and businesses to invest, grow, and improve their financial situations. However, traditional banks often have strict requirements and high interest rates, making it difficult for marginalized communities to access credit. DeFi platforms utilize smart contracts and blockchain technology to facilitate decentralized lending, enabling individuals to borrow and lend funds directly from other users. This creates a more inclusive lending environment and empowers marginalized communities to access much-needed capital for personal and business purposes.
Furthermore, DeFi platforms often use decentralized identity verification systems, eliminating the need for traditional credit scoring systems that may be biased or inaccessible to marginalized communities. This opens up opportunities for individuals with limited credit history to access loans and financial services based on other factors, such as reputation and collateral.
In conclusion, the empowerment of marginalized communities is a significant benefit of the debanking movement and the democratization of finance. By providing access to basic banking services and expanding opportunities for credit and loans, DeFi platforms empower individuals and communities to overcome financial barriers, improve their financial situations, and participate more fully in the global economy.
Economic growth and development
Economic growth and development are closely related to financial inclusion and debanking. When more individuals and businesses have access to financial services and products, it can lead to increased economic activity, job creation, and poverty reduction.
Financial inclusion can empower individuals, particularly those in marginalized communities, by providing them with the tools and resources they need to participate fully in the economy. By allowing individuals to save money, access credit, and make payments, financial inclusion can help break the cycle of poverty and promote economic mobility.
Moreover, when more people have access to financial services, it can foster entrepreneurial activity and encourage investment in productive sectors of the economy. This can lead to increased job opportunities, innovation, and economic growth.
Financial inclusion and economic inequality
While financial inclusion can contribute to economic growth and development, it is important to address any potential risks and challenges. One challenge is the potential for exacerbating economic inequality.
Without appropriate regulations and safeguards, financial inclusion can disproportionately benefit those who are already economically advantaged, while leaving behind the most vulnerable and marginalized populations. Therefore, it is crucial to ensure that financial inclusion initiatives are designed in a way that promotes equal access and opportunities for all.
Efforts to promote financial inclusion should also be complemented by other initiatives aimed at addressing structural barriers that contribute to economic inequality, such as education, health care, and social support systems.
The role of technology in promoting financial inclusion
Advancements in technology, such as mobile banking and digital payment systems, have played a crucial role in expanding financial inclusion. These technologies have made it easier and more cost-effective for individuals, especially those in remote areas, to access financial services.
However, it is important to ensure that the benefits of technology-driven financial inclusion reach all segments of the population, including those who may be digitally excluded due to lack of internet connectivity or digital literacy.
To maximize the potential benefits of technology, governments, financial institutions, and technology companies need to work together to develop and implement inclusive and user-friendly digital financial solutions. This includes investing in infrastructure, promoting digital literacy, and addressing concerns related to data privacy and security.
Overall, financial inclusion and debanking have the potential to drive economic growth and development by empowering individuals and businesses, promoting entrepreneurship, and reducing poverty. However, to ensure sustainable and inclusive growth, it is important to address the challenges and risks associated with these initiatives and to leverage technology in a way that benefits all members of society.
Challenges and risks of debanking
As the process of debanking continues to gain momentum, it is crucial to examine the challenges and risks that may arise from this democratization of finance. While debanking offers numerous benefits, such as increased financial inclusion and the potential for greater transparency, it is not without its drawbacks.
One of the primary challenges of debanking is the potential for increased financial vulnerability. As traditional banking services are removed or limited, individuals may be left without access to essential financial tools, such as savings accounts, loans, and insurance. This can create a significant gap in financial security, particularly for marginalized communities who rely heavily on traditional banking services.
Additionally, the absence of banking services can lead to a rise in informal financing methods, which may be unregulated and risky. Without the oversight and consumer protections provided by formal banking institutions, individuals may fall victim to predatory lending practices or financial scams. This can further exacerbate financial inequality and leave individuals more susceptible to economic instability.
Furthermore, debanking can pose challenges in terms of data privacy and security. As more individuals turn to alternative financial platforms and applications, there is an increased risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to personal information. This can have severe consequences, including identity theft and financial fraud, which can undermine trust in the financial system.
Lastly, debanking may also result in a digital divide, where certain segments of the population are excluded from accessing digital financial services. This can occur due to limited internet access, lack of technical knowledge, or language barriers. As a result, those who are already financially excluded may face further marginalization, as they are unable to take advantage of the opportunities provided by debanking.
| Challenges and risks of debanking: |
|---|
| Increased financial vulnerability |
| Rise in informal financing methods |
| Data privacy and security concerns |
| Digital divide |
Exclusion of certain populations
While the democratization of finance promises greater inclusion and access to financial services for all, it is important to recognize that certain populations may face exclusion from these benefits. This exclusion can be attributed to various factors such as social, economic, and cultural barriers.
One population that often faces financial exclusion is the unbanked and underbanked. These individuals may not have access to traditional banking services due to factors such as lack of identification documents, low income, or being deemed as high-risk customers. Without access to bank accounts, they are unable to take advantage of services such as loans, savings accounts, and insurance, leaving them in a vulnerable financial position.
Another population that may face exclusion is individuals in rural or remote areas. These areas often have limited financial infrastructure, making it difficult for individuals to access banking services. Limited access to physical bank branches and ATMs can make it challenging to deposit or withdraw money, hindering their ability to participate in the formal financial system.
Furthermore, certain cultural factors may also contribute to the exclusion of populations from the democratization of finance. In some communities, there may be a mistrust of formal financial institutions, leading individuals to rely on informal financial networks or cash-based transactions. This can result in limited access to credit, insurance, and other financial services that are vital for economic growth and stability.
It is crucial to address these barriers and strive for greater financial inclusion to ensure that everyone has equal opportunities to access and benefit from financial services. Efforts towards digitalization, financial literacy, and innovative solutions can help overcome these challenges and bridge the gap for excluded populations, promoting a more inclusive and equitable financial system.
Data privacy and security concerns
In the era of digital finance, data privacy and security have become major concerns for individuals and organizations alike. As more transactions and financial activities are being conducted online, there is a growing need to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access and potential misuse.
One of the main concerns of financial inclusion and debanking is the collection and storage of personal data. While the democratization of finance aims to provide equal access to financial services, it also requires individuals to share their personal and financial information with various institutions, such as banks and fintech companies.
However, this increased sharing of data raises questions about privacy and security. Individuals may worry about the potential misuse of their personal information, such as identity theft or unauthorized access to their bank accounts. Additionally, data breaches and cyberattacks have become more common, posing a risk to the security of individuals’ financial data.
To address these concerns, governments and financial institutions need to prioritize data privacy and security. This includes implementing robust security measures to protect individuals’ data, such as encryption and multi-factor authentication. It also involves educating individuals about the importance of data privacy and providing them with the tools and knowledge to protect their information.
Furthermore, regulations and policies should be established to govern the collection, use, and storage of individuals’ data. These should include clear guidelines on how data can be used, who has access to it, and how it can be protected. Individuals should have the right to know what data is being collected about them and have control over its use.
Overall, while debanking and financial inclusion offer numerous benefits, it is crucial to address data privacy and security concerns to ensure the trust and confidence of individuals in the financial system. Only then can the democratization of finance truly benefit everyone.
Regulatory implications
The democratization of finance through debanking and the rise of financial inclusion has significant regulatory implications. As more people have access to financial services, it becomes crucial for regulators to ensure that these services are safe and transparent. Regulatory frameworks need to be adapted to keep up with the pace of innovation and protect consumers from fraud and harmful practices.
One key regulatory implication is the need to establish guidelines for digital identity verification. With the increasing adoption of digital financial services, it is essential to have effective systems in place to verify the identity of customers and prevent money laundering and other illicit activities. This may involve working in collaboration with technology companies and leveraging advanced solutions such as biometrics and artificial intelligence to enhance security and maintain trust in the financial system.
Another important aspect is the regulation of digital currencies and decentralized finance. As cryptocurrencies gain popularity and decentralized finance platforms become more prevalent, regulators are faced with the challenge of ensuring financial stability while also fostering innovation. Clear guidelines and standards are needed to address issues such as risk management, consumer protection, and market integrity in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Additionally, regulators must consider the potential for new forms of financial exclusion to arise as debanking and digital finance become more widespread. While these innovations have the potential to increase financial inclusion, there is a risk that certain individuals or communities may be left behind due to limited access to technology or lack of financial literacy. It is therefore crucial for regulators to support initiatives that bridge the digital divide and promote financial education to ensure that everyone can benefit from the democratization of finance.
| Regulatory implications highlighted: |
|---|
| Digital identity verification |
| Regulation of digital currencies and decentralized finance |
| Preventing new forms of financial exclusion |
Strategies for addressing the challenges
As the world moves towards a more inclusive financial system through debanking, there are several strategies that can be implemented to address the challenges that arise:
1. Collaboration between financial institutions and fintech companies
One strategy is to encourage collaboration between traditional financial institutions and fintech companies. This collaboration can help leverage the strengths of both sectors to address the challenges of debanking and financial inclusion. For example, financial institutions can provide the regulatory expertise and customer base, while fintech companies can bring innovation and new technologies to the table.
2. Investment in digital infrastructure
Another strategy is to invest in digital infrastructure to support the democratization of finance. This includes improving internet connectivity, expanding mobile network coverage, and promoting digital literacy. By investing in digital infrastructure, marginalized communities and individuals in remote areas can gain access to financial services and products.
3. Regulatory frameworks and policies
Regulatory frameworks and policies play a crucial role in addressing the challenges of debanking and financial inclusion. Governments and regulators need to create an enabling environment that fosters innovation while ensuring consumer protection. This includes developing clear guidelines for fintech companies, establishing risk management frameworks, and promoting transparency and accountability in the financial system.
4. Education and awareness programs

Education and awareness programs are essential to ensure that individuals understand the benefits and risks of debanking and financial inclusion. These programs can help build trust in digital financial services and promote financial literacy. By providing individuals with the necessary knowledge and skills, they can make informed financial decisions and navigate the digital financial landscape effectively.
By implementing these strategies, the challenges of debanking and financial inclusion can be addressed, and the democratization of finance can benefit a larger portion of the population.
Improving access to education and technology
The democratization of finance through debanking has the potential to improve access to education and technology for individuals who have historically been underserved by traditional financial institutions. By providing alternative financial services, debanking allows individuals to save and invest their money in ways that were previously inaccessible. This newfound financial freedom enables them to pursue educational opportunities and access technology that can further their personal and professional development.
Education
Access to quality education is often limited by financial constraints. Traditional financial institutions have strict requirements for loans and credit, making it difficult for those with low income or no credit history to access funding for education. Debanking provides an alternative by offering microloans, crowdfunding platforms, and peer-to-peer lending. These services enable individuals to access funds for educational purposes without the need for a traditional bank. Additionally, debanking platforms can connect individuals with financial literacy programs and educational resources that promote financial well-being and economic empowerment.
Technology
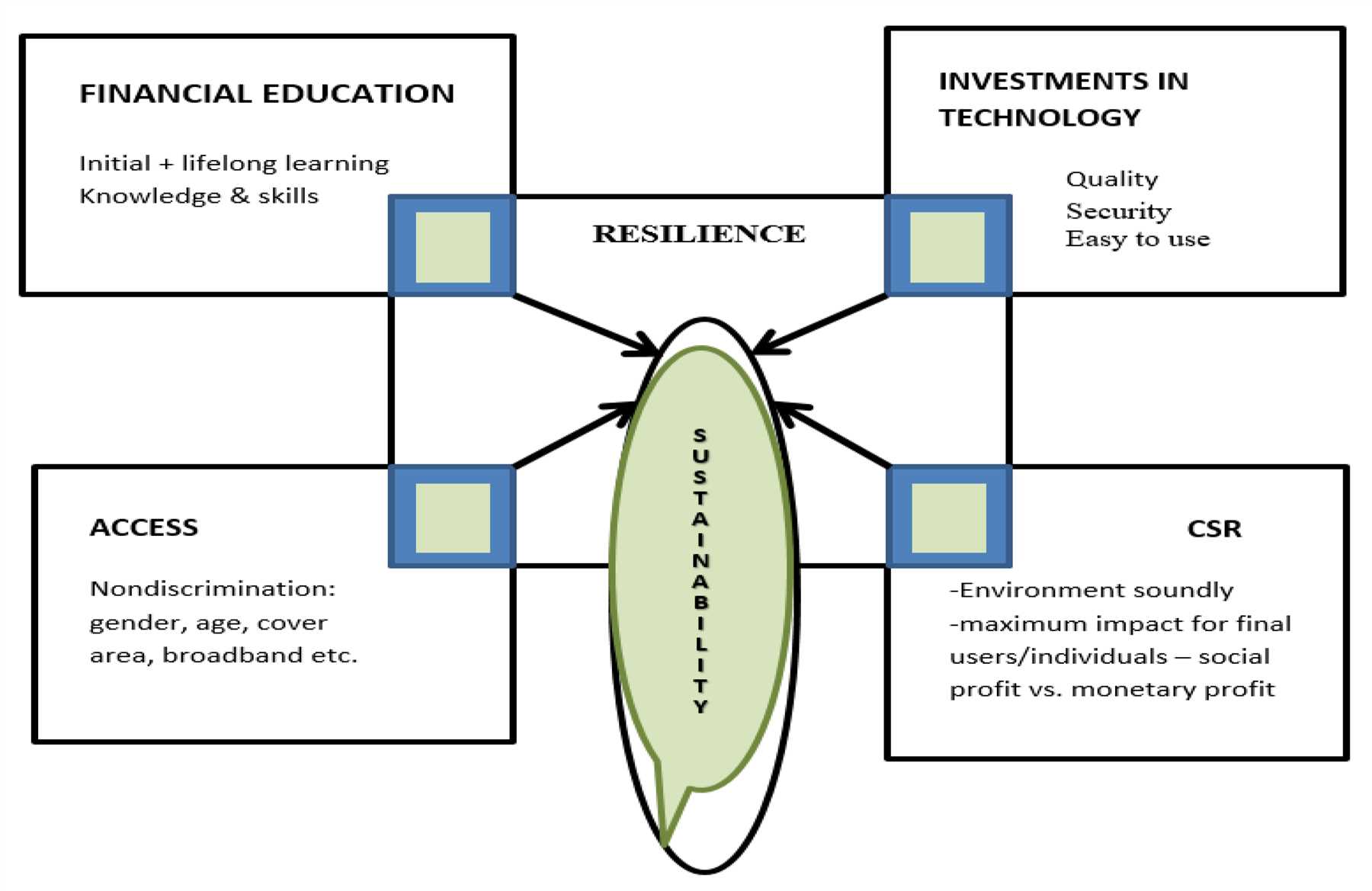
In today’s digital age, access to technology is essential for personal and professional development. However, many underserved populations lack the means to purchase or access technology devices and services. Debanking can bridge this gap by offering affordable financing options for technology purchases, such as smartphones, computers, and internet services. Additionally, debanking platforms can collaborate with technology providers to offer discounts and incentives to their users, making technology more accessible and affordable for all. By improving access to technology, debanking contributes to digital inclusion and opens up opportunities for individuals to acquire new skills, access online educational resources, and participate in the digital economy.
In conclusion, the democratization of finance through debanking can significantly improve access to education and technology for underserved individuals. By providing alternative financial services, debanking expands opportunities for educational advancement and technological inclusion, empowering individuals to enhance their knowledge, skills, and socio-economic well-being.
Strengthening regulations and consumer protection
As the democratization of finance continues to reshape the financial landscape, it is essential to strengthen regulations and consumer protection measures to safeguard individuals and promote a fair and transparent system. This will ensure that the benefits of debanking and financial inclusion are extended to all members of society, including those who may be vulnerable or lack financial literacy.
Enhanced regulatory frameworks
In order to foster a more inclusive and sustainable financial system, regulatory bodies need to adapt and evolve. This involves creating frameworks that address the unique challenges and risks associated with debanking and financial inclusion. Regulations should aim to strike a balance between promoting innovation and protecting consumers, while also taking into account the diverse needs and circumstances of individuals.
Governments and regulatory authorities can strengthen regulations by implementing measures such as:
| 1. Transparency requirements | 2. Lending practices |
|---|---|
| Requiring financial institutions to provide clear and easily understandable information about their products and services, including fees, charges, and terms. | Introducing guidelines to ensure responsible lending practices, which include assessing borrowers’ ability to repay loans and preventing predatory lending. |
| 3. Consumer education | 4. Data protection |
| Investing in financial literacy programs to empower individuals with the knowledge and skills to make informed financial decisions. | Establishing robust data protection measures to safeguard consumers’ personal and financial information from unauthorized access or misuse. |
Consumer protection measures
Alongside regulatory frameworks, consumer protection measures play a crucial role in ensuring the inclusivity and fairness of the financial system. Governments and regulatory authorities should implement policies to protect consumers from deceptive practices, fraud, and discrimination.
Some key consumer protection measures include:
- Creating avenues for individuals to file complaints and seek redress for financial malpractices.
- Establishing mechanisms for monitoring and enforcing compliance with regulations to hold financial institutions accountable.
- Promoting financial literacy initiatives to equip consumers with the knowledge and skills to make informed decisions and protect themselves from financial risks.
- Developing frameworks to address the digital divide and ensure that technological advancements do not exacerbate inequalities.
By strengthening regulations and consumer protection measures, society can harness the transformative potential of debanking and financial inclusion while minimizing the risks and ensuring that the benefits are inclusive and sustainable for all.
FAQ:,
What is debanking and how does it affect financial inclusion?
Debanking refers to the practice of denying financial services to certain individuals or businesses. This can include denying access to bank accounts, loans, or other financial tools. Debanking can have a negative impact on financial inclusion, as it effectively excludes certain populations from participating in the formal financial system.
Who are the main beneficiaries of the democratization of finance?
The democratization of finance aims to benefit all individuals and businesses by providing equal access to financial services. However, certain populations may benefit more, such as those who have historically been marginalized from the traditional financial system. This includes low-income individuals, small businesses, and those in underserved communities.
How does debanking affect small businesses?
Debanking can have a significant negative impact on small businesses. Without access to banking services, these businesses may struggle to receive or make payments, secure loans, or manage their finances efficiently. This can hinder their growth and overall success, making it more difficult for them to compete with larger, more established businesses.
What are the potential solutions to debanking and promoting financial inclusion?
There are several potential solutions to debanking and promoting financial inclusion. One approach is to encourage the development and use of alternative financial services, such as mobile banking or digital wallets. Another solution is to implement regulations and policies that prevent discriminatory practices by financial institutions. Additionally, financial literacy programs can help educate individuals about their rights and options when it comes to accessing financial services.
What are the risks associated with the democratization of finance?
The democratization of finance can come with risks, such as an increase in fraudulent activities, as more individuals gain access to financial services. There is also the risk of over-indebtedness, as some individuals may take on more debt than they can afford. Additionally, the democratization of finance may lead to the displacement of traditional financial institutions, potentially causing job losses and economic instability.